Prostatitis is a disease of the prostate gland (prostate), developing a result of inflammatory changes in the. According to statistics, the prevalence rate of the disease has reached 35% to 50% and common in men aged 20 to 40 years.
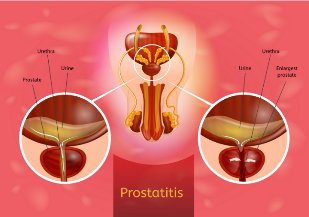
Types of
Secrete 4 forms of prostatitis:
- acute (bacterial);
- chronic bacterial;
- chronic non-bacterial;
- asymptomatic chronic.
Prostatitis acute is very rare because of the rapid current of the inflammatory process and the more immediate transition to a chronic stage (lje improvement).
Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis, otherwise known as the syndrome of chronic pelvic pain, can have inflammatory (with the presence in the urine and the ejaculate content of white blood cells) and is not of an inflammatory nature.
The reasons
The cause of acute and chronic prostatitis bacterial are pathogenic agents (viruses, bacteria, fungi). Most often the source of inflammation are:
- escherichia coli;
- streptococci;
- staph;
- proteus;
- klebsiella;
- pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, mycoplasma, gonococci, trichomonas, cytomegalovirus, and others).
A large part of the micro-organisms found in the bowels, the skin is reactive, but, entering the tissue of the prostate, they trigger an inflammatory process. Generally, the cause of the disease is not a pathogen, and the combination of several types of microbes.
The development of the chronic prostatitis can cause the following factors:
- diseases of the urinary tract (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- sedentary lifestyle ("sedentary" work);
- tendency to constipation;
- the weakening of the body's defenses;
- injuries;
- a hormonal imbalance;
- the abuse of alcohol and smoking;
- promiscuity;
- intermittent sex life (duration of abstinence);
- coitus interruptus;
- irregular emptying of the bladder;
- dissatisfied with the sexual desire;
- the chronic stress;
- hypothermia;
- the presence of carious teeth and other sources of chronic infection (eg, chronic tonsillitis).
The symptoms of prostatitis
Prostatitis acute is a very insidious disease. To "catch" the sound difficult enough as it is, first of all, the process is very fast becoming chronic, and on the other hand, most patients prefer the "overflow" of the manifestation of prostatitis acute of the house. A doctor, patients with an inflammation of the prostate often turn already in the case of erectile dysfunction, and other consequences.
The acute form of the disease occurs on the background:
- increase of the temperature;
- chills;
- other signs of intoxication (weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, etc).
The inflammation of the prostate is accompanied by pain in the crotch, the groin and into the scrotum.
Characteristic also painful and increased urination. Sometimes in the urine, you may notice a whitish purulent.
In addition, the patient can draw attention to the lack of boxes of night and morning erections, poor quality of erection during the intimacy and the strong shortening of the sexual act.
The signs of prostatitis chronic bacterial may be missing, or appear in periods of exacerbation. During this phase are characteristics of pain in the region of the groin and abdomen, they are often radiating to the sacrum, the lower back and scrotum.
Appear the typical symptoms of disorders of urination: weak urine stream and frequent urination, although the urine stands out a bit.
Subsequently, in the absence of treatment of chronic prostatitis reaches its climax: will appear disorders of the sexual function. For example:
- the lack of erection or its absence;
- painful erections, due to which the patient is to avoid sexual acts;
- erosion excessive orgasm;
- short of the sexual act;
- the pain of the ejaculation.
Leaves something to be desired, and the general state of men: he tires quickly, constantly annoyed, trouble sleeping.
Chronic abakterialniy prostatit is 95% of prostatitis, falling sick, they were mostly men of about 30 years. It is characterized by constant or pain in the pelvic area, the prostate, the scrotum, and the laboratory analyses are absent signs of inflammation. The causes of the disease is not installed.
The diagnosis
At the time of diagnosis acute and chronic prostatitis, in addition to the collection of complaints, anamnesis and examination of the patient using the following methods:
- total analysis of blood and urine;
- the microscopic examination of the secretions of the prostate and seeding on nutrient medium to identify the pathogen (the secret receive after the touch followed by a massage of the prostate through the rectum);
- the urinary cytology;
- ULTRASOUND of the prostate and the pelvic organs;
- the computed tomography and nuclear-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- the removal of the urethra on the microflora.
The differential diagnosis is focused on the delimitation of the prostatitis, adenoma of the prostate, prostate cancer, signs of stones in the prostate gland.
The full list of diagnostic procedures and drugs for the treatment of prostatitis of the Federal standard using 2012.
Treatment of prostatitis
The same symptoms can be signs of various diseases and the disease is not in the manual. Do not try to medicate themselves — speak with your doctor.
The treatment of prostatitis leads to a surgeon urologist.
The aim of causal treatment aimed at eliminating the causes of prostatitis, is the elimination of the pathogen. The identification of the causes of antibiotics are prescribed, antiviral or anti-fungal. The duration of therapy for prostatitis and acute is 7 to 10 days, in the process of 4-8 weeks.
For the treatment of a bacterial infection are used:
- antibiotics fluoride the quinoline series (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin);
- macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin);
- doxycycline;
- antibacterial drugs.
Antifungals are appointed by the oral and rectal in the candlelight.
In addition, it uses other types of therapy:
- anti allergic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- relief of the pain.
Are also prescribed:
- physio;
- physiotherapy;
- the massage of the prostate.
All treatment is 3-4 months.
Complications
Is not cured of prostatitis dangerous complications of the following:
- an obstruction of the bladder follow-up of an acute urinary retention;
- the sterility;
- recurrent inflammation of the bladder;
- an abscess of the prostate;
- depression;
- impotence;
- the adenoma of the prostate;
- calculous prostatitis (stone like with debilitating pain);
Forecast
Forecast for prostatitis is acute favorable, early treatment leads to full recovery. The frequency of exacerbations in chronic prostatitis reaches 50% and more, but if it supports the treatment to achieve a remission stable.
Prevention
For the prevention of the disease, you must meet the following conditions:
- the regular sexual life, permanent partner;
- the refusal of bad habits;
- a healthy lifestyle (sports, hiking in the open air);
- compliance with the diet;
- the regular visits to the urologist.
































